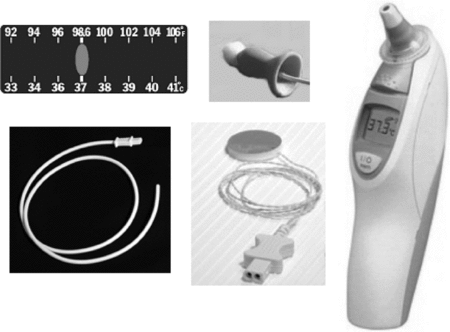
Tympanic membrane pulmonary artery distal esophagus nasopharynx is used to monitor intraoperative hypothermia prevent overheating and facilitate detection of malignant hyperthermia because these sites are not necessarily available or convenient a variety of near core sites are also used clinically.
Temperature monitoring devices in anaesthesia.
Palpation of a pulse auscultation of heart sounds monitoring of a tracing of intra arterial pressure ultrasound peripheral pulse monitoring or pulse plethysmography or oximetry.
Core temperature monitoring e g.
Temperature monitoring devices are relatively inexpensive.
Specialized monitors for obtaining more detailed and complicated information mostly about the heart can also be used when useful or needed for certain types of surgeries.
Temperature and cardiac events.
On average core temperature drops 1 1 5c in the first hour.
Body temperature should be monitored perioperatively every 5 to 10 minutes until the patient has recovered to sternal recumbency and body temperature is maintained between 99 f to 102 f.
Another reason for failing to monitor temperature is that fever is said to be a late sign of malignant hyperthermia.
If a polychromatic infrared detector is used 7 13 um the monitor can automatically detect the anesthetic agent used as the absorption spectra at these wavelengths are relatively different.
4 2 3 every patient receiving general anesthesia shall have in addition to the above circulatory function continually evaluated by at least one of the following.
Mild hypothermia can delay recovery from anesthesia.